Table Of Content
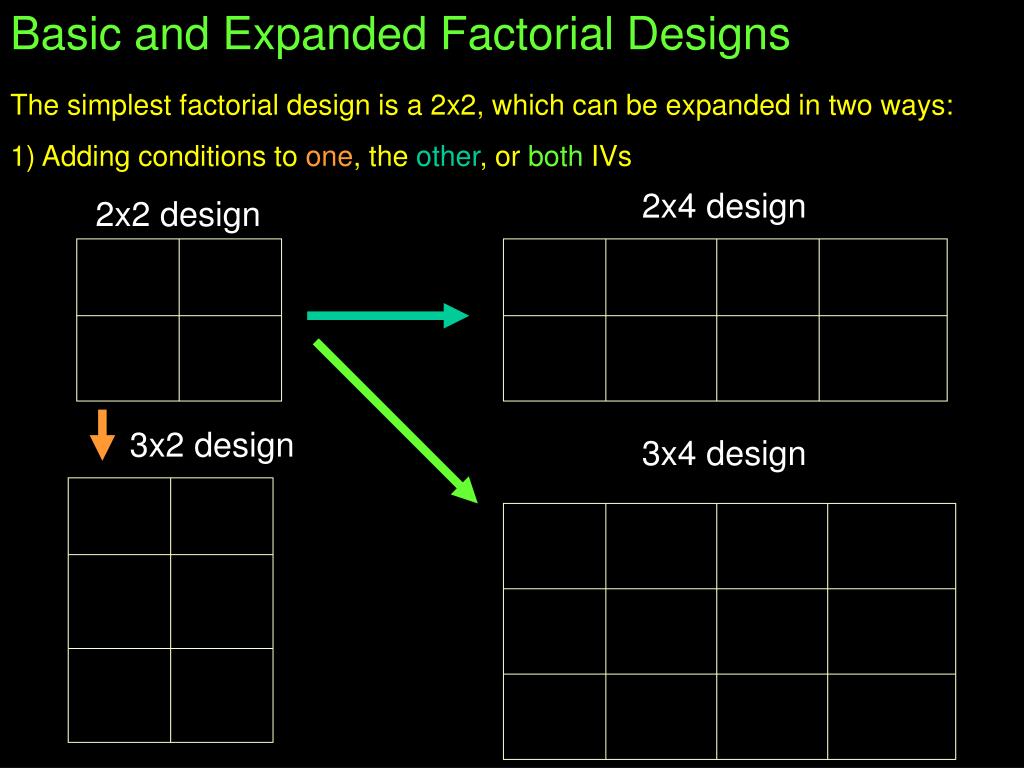
It is also possible to manipulate one independent variable between subjects and another within subjects. Just as it is common for studies in education (or social sciences in general) to include multiple levels of a single independent variable (new teaching method, old teaching method), it is also common for them to include multiple independent variables. As we will see, interactions are often among the most interesting results in empirical research. In principle, factorial designs can include any number of independent variables with any number of levels.
2. Multiple Independent Variables¶
(In reality, there was no other participant.) Then they gave each participant 10 points (which could later be converted to money) to split with the “partner” in whatever way he or she decided. Because the participants were the “dictators,” they could even keep all 10 points for themselves if they wanted to. Remember, an interaction occurs when the effect of one independent variable depends on the level of the other independent variable.
1: Factorial Designs
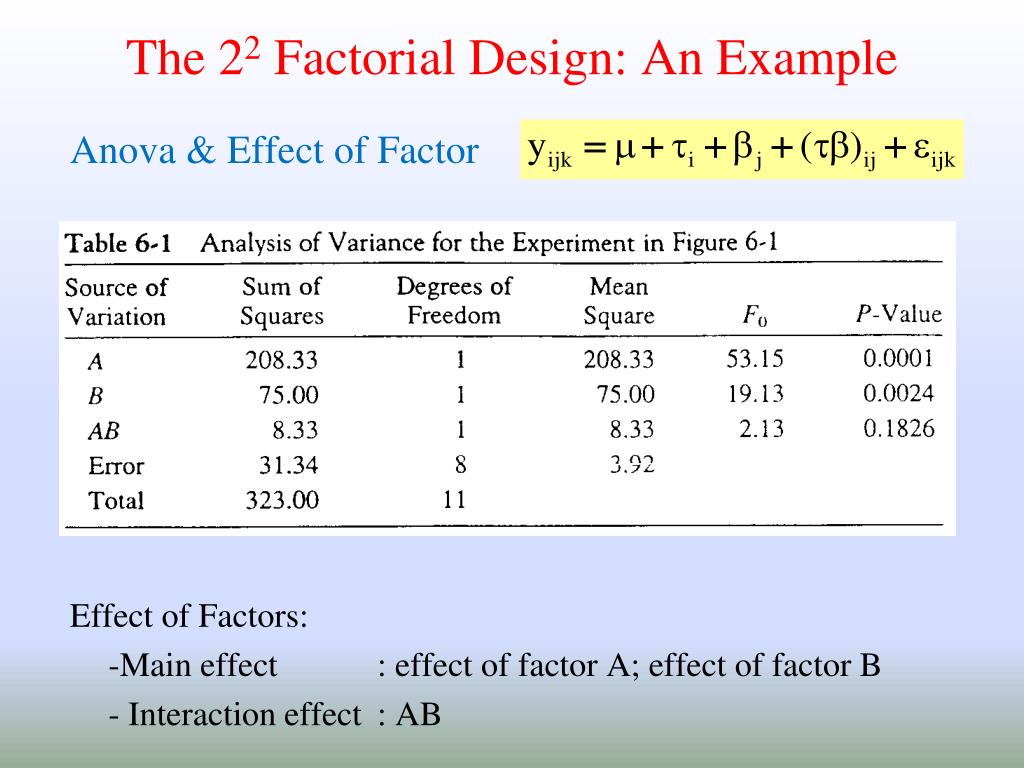
For instance, relative to some complex interactions, main effects are more easily interpreted (Collins et al., 2014); a factor’s main effects are interpretable even when it interacts with other factors. When effect coding is used, each effect is orthogonal to every other effect in the analysis model (orthogonal when the n’s are equal in each experimental condition, and nearly orthogonal when the n’s differ by a modest amount). Thus, a significant main effect reflects an experimental effect that occurs on average across all other factors in the model even when the relevant factor is involved in significant interactions (Chakraborty et al., 2009). Higher order interactions can reflect complex patterns that defy easy interpretation. However, they also reveal information that is unique and of potentially great value.
Minitab Example for Centrifugal Contactor Analysis
This can pose interpretive challenges as it may be difficult to separate the effects of a component per se from the impact of burden. Factorial design is a type of research methodology that allows for the investigation of the main and interaction effects between two or more independent variables and on one or more outcome variable(s). Factorial designs are so useful because they allow researchers to find out what kinds of variables can cause changes in the effects they measure. We measured the distraction effect, then we found that reward causes changes in the distraction effect.
For example, people are either low in hypochondriasis or high in hypochondriasis; they cannot be in both of these conditions. In many factorial designs, one of the independent variables is a non-manipulated independent variable. One independent variable was disgust, which the researchers manipulated by testing participants in a clean room or a messy room.
4. Complex Correlational Designs¶
In many studies, the primary research question is about an interaction. The study by Brown and her colleagues was inspired by the idea that people with hypochondriasis are especially attentive to any negative health-related information. This led to the hypothesis that people high in hypochondriasis would recall negative health-related words more accurately than people low in hypochondriasis but recall non-health-related words about the same as people low in hypochondriasis. The effect of one independent variable can depend on the level of the other in several different ways.
Pyrolysis of domestic sewage sludge: influence of operational conditions on the product yields using factorial design - ScienceDirect.com
Pyrolysis of domestic sewage sludge: influence of operational conditions on the product yields using factorial design.
Posted: Tue, 17 May 2022 18:21:11 GMT [source]
Factorial design is an important method to determine the effects of multiple variables on a response. Traditionally, experiments are designed to determine the effect of ONE variable upon ONE response. Fisher showed that there are advantages by combining the study of multiple variables in the same factorial experiment. Factorial design can reduce the number of experiments one has to perform by studying multiple factors simultaneously. Additionally, it can be used to find both main effects (from each independent factor) and interaction effects (when both factors must be used to explain the outcome). However, factorial design can only give relative values, and to achieve actual numerical values the math becomes difficult, as regressions (which require minimizing a sum of values) need to be performed.
Book traversal links for Lesson 5: Introduction to Factorial Designs
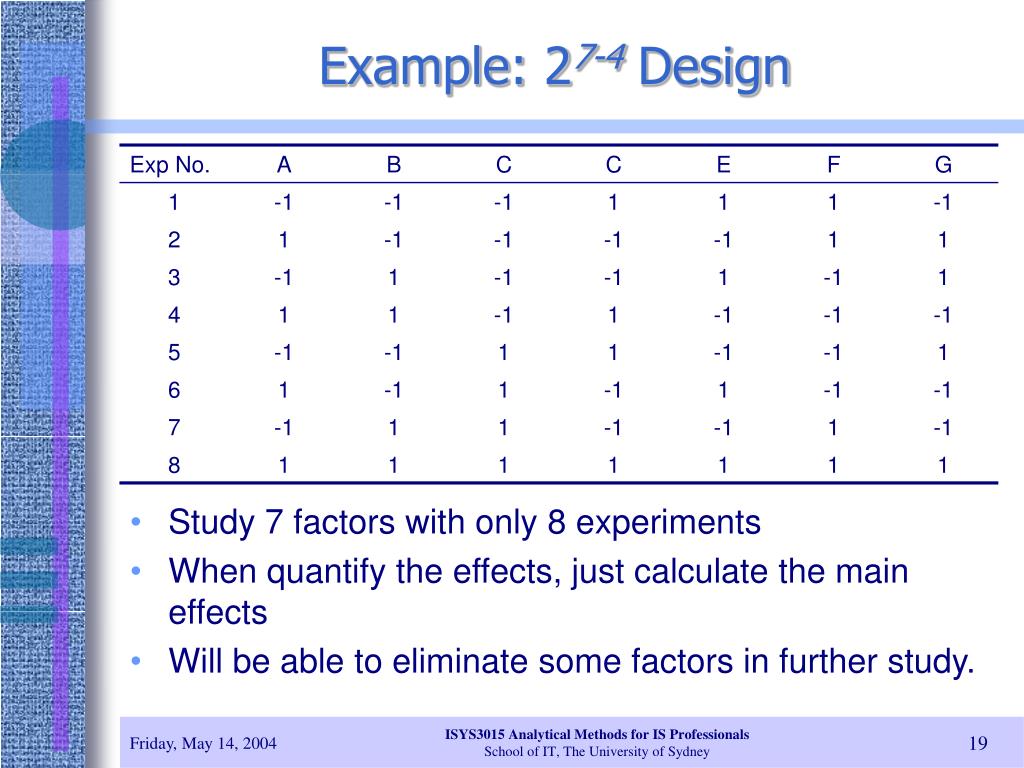
Under this assumption, estimates of such high order interactions are estimates of an exact zero, thus really an estimate of experimental error. This can be conducted with or without replication, depending on its intended purpose and available resources. It will provide the effects of the three independent variables on the dependent variable and possible interactions. A fractional factorial design uses a subset of a full factorial design, so some of the main effects and 2-way interactions are confounded and cannot be separated from the effects of other higher-order interactions. Usually experimenters are willing to assume the higher-order effects are negligible in order to achieve information about main effects and low-order interactions with fewer runs.
3.5. Identifying main effects and interactions¶
The within-subjects design is more efficient for the researcher and controls extraneous participant variables. This would mean that each participant was tested in one and only one condition. The advantages and disadvantages of these two approaches are the same as those discussed in Chapter 4). The between-subjects design is conceptually simpler, avoids carryover effects, and minimizes the time and effort of each participant. The within-subjects design is more efficient for the researcher and help to control extraneous variables. Since factorial designs have more than one independent variable, it is also possible to manipulate one independent variable between subjects and another within subjects.
Once the terms have been chosen, the next step is determining which graphs should be created. The types of graphs can be selected by clicking on "Graphs..." in the main "Analyze Factorial Design" menu. In the "Modify Design" menu, users can modify factors, replicate design, randomize design, renumber design, fold design, and add axial points. To change the factors, click the "Modify factors" radio button and then "Specify" to see the following options menu. The last four column vectors belong to the A × B interaction, as their entries depend on the values of both factors, and as all four columns are orthogonal to the columns for A and B.
Design development of sustainable brick-waste geopolymer brick using full factorial design methodology - ScienceDirect.com
Design development of sustainable brick-waste geopolymer brick using full factorial design methodology.
Posted: Fri, 17 Mar 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
However, you cannot model the effect of that curvature anywhere but at the center point. In other words, you can only calculate the fitted values at the corner points and the center point of the design, and thus cannot create a contour plot. You need to have quadratic terms (for example, square terms) in the model in order to model the curvature across the whole response surface. You can augment the factorial design with axial points to create a central composite response surface design from a factorial design.
Recall that in a simple between-subjects design, each participant is tested in only one condition. In a simple within-subjects design, each participant is tested in all conditions. In a factorial experiment, the decision to take the between-subjects or within-subjects approach must be made separately for each independent variable. In a between-subjects factorial design, all of the independent variables are manipulated between subjects. For example, all participants could be tested either while using a cell phone or while not using a cell phone and either during the day or during the night.
Fractional factorial designs are a good choice when resources are limited or the number of factors in the design is large because they use fewer runs than the full factorial designs. The researchers then decided to look at three levels of sleep (4 hours, 6 hours, and 8 hours) and only two levels of caffeine consumption (2 cups versus no coffee). The researchers note that the effects of the memory drug are more pronounced with the simple memory tasks, but not as apparent when it comes to the complex tasks. In this 3×2 factorial design, there is an interaction effect between the drug dosage and the complexity of the memory task. As we have already seen, researchers conduct correlational studies rather than experiments when they are interested in noncausal relationships or when they are interested variables that cannot be manipulated for practical or ethical reasons. In this section, we look at some approaches to complex correlational research that involve measuring several variables and assessing the relationships among them.

No comments:
Post a Comment